Recommended Cisco Meraki Firewall Settings
Get expert advice on setting up your Cisco Meraki Firewall for optimal security and performance of your VoIP System.
Table of Contents
Quick Tip:
The Cisco support site has documentation on how to best setup a Cisco Meraki firewall:
Voice over IP (VoIP) is a common technology used in enterprise networks, allowing users on a network to make internal and outbound phone calls over the network. This article outlines a number of frequently asked questions regarding VoIP systems and technologies on Cisco Meraki networks, as well as some general troubleshooting tips and tricks.
Recommended Subnet and Port Configuration
Read the sections below to allow traffic from the services in use by your company. If you not using a specific service, such as Stratus users that do not use our Enswitch platform and vice versa, you can avoid opening the ports used by that service.
Note: If you are not sure which services you are using and which ports and subnets should be opened, contact your Installer or our Technical Support team for more information.
SpectrumVoIP Public Subnets
- 199.71.209.0/24
- 24.227.249.0/25
- 72.249.136.32/28
- 206.123.122.32/27
- 212.69.157.32/27
- 40.143.31.64/27
- 45.41.5.0/24
- 12.150.91.0/24
Ports - Stratus Platform
IMPORTANT: These ports only need to be opened if you are utilizing our Stratus platform. If you are using our Enswitch (ES) platforms, these ports do not need to be opened.
If your company does not use the StratusHUB desktop app, the SpectrumVoIP Stratus mobile app, StratusMEETING, or StratusWEB PHONE, the ports/subnets for those services do not need to be allowed or opened.
If you are not sure which services you are utilizing, contact your Installer or our Technical Support team for more information.
Main Utilized Ports
- 5060-5062 UDP - SIP
- 20,000-40,000 UDP - RTP
- 80, 443 TCP - HTTP/HTTPS
Portal Dynamic Updates
- 8001 - TCP
Text-to-Speech Services - TCP and UDP
- 35.175.185.150:3001
- 35.175.185.150:8000
- 44.212.88.215:8000
- 54.149.243.27:3001
- 54.149.243.27:8000
- 54.70.235.134:3001
- 54.70.235.134:8000
StratusFAX 2.0 - TCP
- 5066 TCP - HTTPS and HTTP
REMINDER: If your company does not pay for and use StratusFAX 2.0, the port for this service does not need to be opened.
StratusMEETING - TCP and UDP
REMINDER: If your company does not use StratusMEETING, the subnets for this service do not need to be allowed.
- 54.188.133.147:3443
- 3.130.158.184:3443
- 35.183.150.146:3443
StratusHUB Desktop App
REMINDER: If your company does not use the StratusHUB desktop app, the port for this service does not need to be opened.
- 8082 - TCP
StratusWEB PHONE
REMINDER: If your company does not use StratusWEB PHONE, the port for this service does not need to be opened.
- 9002 - TCP - websockets
Ports - Enswitch 1 and 2 Platforms
IMPORTANT: These ports only need to be opened if you are utilizing one of our Enswitch (ES1 or ES2) platforms. If you are using our Stratus platform, these ports do not need to be opened.
If you are not sure which service you are utilizing, contact your Installer or our Technical Support team for more information.
- 5060-5062 UDP - SIP
- 10,000-20,000 UDP - RTP
- 80, 443 TCP - HTTP/HTTPS
Push Notifications Ports
IMPORTANT: If your users are using our softphone mobile apps on cellular devices or tablets connected to the office's Wi-Fi network, it is recommended to open these ports on the firewall equipment so that push notifications for the apps are not blocked.
Android and Google Devices - Google's Firebase Cloud Messaging, aka FCM
- 443, 5228, 5229, 5230 - TCP
More Info: Ports 5228, 5229, and 5230 are the primary ports used by Google's Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM) service for mobile devices to receive push notifications.
Apple Devices - Apple Push Notification Service, aka APNs
- 5223, 443, 2197 - TCP
More Info: Port 5223 is the primary port for communication used by Apple's Push Notification Service (APNs).
Ports 443 and 2197 are used for sending notifications from Mobile Device Management (MDM) software to APNs and as a fallback on Wi-Fi if port 5223 cannot be utilized.
How Do I Optimize VoIP Services with Cisco Meraki Devices?
Since Cisco Meraki equipment is designed with network standards in mind, VoIP deployments can typically be run alongside the network stack with no issues:
The MX
The MX security appliance functions as a standard stateful firewall, performing inter-VLAN routing for the network. Typically, since VoIP traffic is best segregated to its own VLAN, the MX may be configured with a dedicated voice VLAN (assuming the MX is configured as the network's inter-VLAN router).
If the MX has been configured with multiple uplinks, especially if those uplinks are being aggregated, it may be prudent to ensure that voice traffic is only using a particular interface. This can be accomplished using uplink preferences under Security appliance > Configure > Traffic shaping.
Traffic shaping rules can be used to prioritize voice traffic above other traffic types. This is possible since the MX can be configured to be used as a DHCP server to allow IP phones to automatically connect and apply dynamic configuration changes.
For some additional reading on relevant MX configuration and features, check out the following guides by Cisco:
• Configuring VLANs on the MX
• Traffic Shaping for Packet Prioritization
• Configuring DHCP Options
• Link Aggregation and Uplink Preferences
The MS
Cisco Meraki switches are standards-based network switches, designed for the access and distribution layers of the network. On the access layer, access switch ports can be configured with a "Voice VLAN," where the MS will use LLDP to advertise the voice VLAN's ID to the connected phone. This may not work for all VoIP hardware; the ideal configuration will depend on the specific phone in use, please refer to your phone documentation to determine the optimal configuration at the access layer.
If a layer-3 MS switch is performing inter-VLAN routing, a configuration of a dedicated voice VLAN may be done on that switch.
For some additional reading on relevant MS configuration and features, read the following guides from Cisco:
• VoIP Deployment on MS Access Switches
• Layer 3 Configuration Overview
The MR
If some wireless voice infrastructure is needed, additional steps should be taken during wireless deployment to ensure a stable roaming environment. In particular, a wireless site survey is strongly recommended to ensure ideal placement and configuration of APs, thereby allowing for a clean RF environment for your wireless phones to roam.
If the voice SSID is using enterprise 802.1X authentication (and the technology is supported by the wireless phone hardware), it may be beneficial to enable fast roaming (802.11r) on the MR access points to improve roaming times between access points.
For some additional reading on relevant MR configuration and features, read the following guides provided by Cisco:
• Performing a Wireless Site Survey
• Fast Roaming Technologies
What are Some Best Practices for Using VoIP?
While managing your network and its infrastructure, it is best to ensure your equipment is securely implemented with a consideration for how your VoIP-reliant devices, like desk phones, are able to optimally function on your network. Read the sections below to review recommended, best practices to follow while using IP desk phones.
Segregate IP Phones into a Voice VLAN
Voice traffic tends to come in large amounts of two-way UDP communication. Since there is no overhead on UDP traffic, voice traffic is extremely susceptible to bandwidth limitations, clogged links, or even just non-voice traffic on the same line.
Creating a dedicated VLAN for your different groups of IP devices, such as your desk phones, is a great way to simplify managing your network and troubleshooting future issues with those devices. It is generally recommended to use VLANs to isolate IP devices to reduce the risk of unauthorized access to these devices and limit the spread of potential threats within your network. Segmenting a network using VLANs can also help reduce congestion and improve a network's overall performance, which can be a great boon for networks with many VoIP devices.
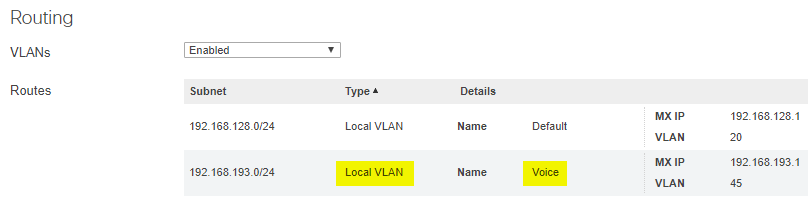
Manual Port Configuration
This is the most basic method, requiring explicit, per-port configuration by a network administrator. It is typically used when automated discovery is not available or desired. The switch port must be configured as an access port with a specific voice VLAN setting. The switch is explicitly told to use a specific Data VLAN for untagged traffic (for the connected PC) and a specific Voice VLAN for tagged (802.1Q) traffic. Any traffic arriving on that port that is untagged is placed into the Data VLAN, and any traffic tagged with the Voice VLAN ID is placed into the Voice VLAN. The IP phone must be manually configured (or use a secondary method like DHCP) to tag its voice traffic correctly.
Note: If you choose this method, please provide your installer with the VLAN ID you wish to use so they can add that parameter to your phones' network settings.
Automatic Discovery via LLDP/CDP
If your network switches support Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP), LLDP Media Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED), and/or Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP), Grandstream, Yealink, and Polycom desk phones are compatible with these protocols and can utilize them to be discovered by neighbor devices and switches.
If your network switch does offer LLDP, LLDP-MED, or CDP, it is recommended to ensure these protocols are enabled and configured to point to your desired VLAN. Doing so will allow the switches to discover compatible IP phones and set the devices in a VLAN dynamically depending on the device's configuration information.
What is LLDP-MED?
LLDP-MED is an extension of LLDP that operates between IP phones and network devices, such as switches for voice over IP (VoIP) applications. It does this by sending TLVs.
TLVs (Type-Length-Value) are attributes that describe type, length, and value. Devices that support LLDP can use TLVs to receive and send information with neighboring devices. The information shared using this protocol can be configuration information, device capabilities, and device identity.
Switches that have LLDP-MED enabled can use specialized TLVs that describe discovery capabilities, supported network policies, Power over Ethernet (PoE) capability, and inventory management. This can make connecting and managing IP devices, such as our desk phones, more streamlined.
Option 132 for Yealink Phones
Option 132 in DHCP is a feature that enables automatic VLAN assignment. When a device connects to the network, it sends a DHCP request containing its MAC address. The DHCP server that has Option 132 configured identifies the device and assigns a suitable VLAN.
NOTE: This only works for Yealink brand phones and needs to be made as a custom option on a DHCP Server.
To create a DHCP VLAN option on your DHCP server to allow Yealink phones to automatically connect and provision when plugged in, the following can be configured:
• Option 132: Set Voice VLAN ID
• Type: String (ASCII)
• Value: 'VLANTAG' for example '20' for VLAN 20
This DHCP option should be applied to your native DHCP server so that the phones receive the configuration when first plugged in. This may also be applied to the voice VLAN if needed.
Use Traffic Shaping
Since voice traffic involves the transmission of relatively large amounts of data on the network, it is important to ensure that your voice traffic from desk phones has enough bandwidth to operate. Traffic shaping rules can be implemented to allow voice traffic to use additional bandwidth and limit other types of traffic.
Bandwidth Requirements
Voice-only applications utilize G.711 U-Law as the primary codec and require 87.2 Kbps of bandwidth per active call. A good rule of thumb is to round the requirement up to 100Kbps to account for signaling and overhead.
For example… A 10Mbps/1Mbps ISP connection that is solely dedicated to the phones would support 10 concurrent phone calls.
Use Quality of Service Tags to Prioritize VoIP Traffic
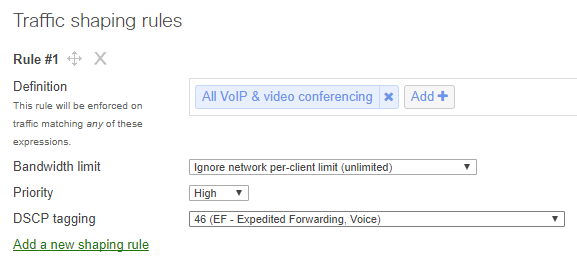
Understand Firewall and NAT Configurations
The MX of a Cisco Meraki is a stateful firewall, so most inbound communication will only be allowed as a response to an established outbound conversation. Inbound communication will need to be allowed by using either port forwarding or 1:1 NAT/1:Many NAT rules.
When a stateful firewall is receiving traffic, it will handle that traffic depending on the source of the communication:
- If an internal phone initiates a connection to an external contact, the stateful firewall will allow the external caller's response back into the network.
- If an external caller attempts to initiate a connection to an internal phone, it will be blocked unless there is a port forward or NAT rule allowing that communication.
To ensure VoIP calls are able to traverse your network to their intended destinations, it is recommended to set up NAT rules that allow traffic to pass through the subnets and ports used by SpectrumVoIP services.
To review the ports and IPs used by SpectrumVoIP services, review the module below:
Recommended Subnet and Port Configuration
SpectrumVoIP Public Subnets
• 199.71.209.0/24
• 24.227.249.0/25
• 72.249.136.32/28
• 206.123.122.32/27
• 212.69.157.32/27
• 40.143.31.64/27
• 45.41.5.0/24
• 12.150.91.0/24
Ports - Stratus Platform
IMPORTANT: These ports only need to be opened if you are utilizing our Stratus platform. If you are using our Enswitch (ES) platforms, these ports do not need to be opened.
If your company does not use the StratusHUB desktop app, the SpectrumVoIP Stratus mobile app, StratusMEETING, or StratusWEB PHONE, the ports/subnets for those services do not need to be allowed or opened.
If you are not sure which services you are utilizing, contact your Installer or our Technical Support team for more information.
Main Utilized Ports
• 5060-5062 UDP - SIP
• 20,000-40,000 UDP - RTP
• 80, 443 TCP - HTTP/HTTPS
Portal Dynamic Updates
• 8001 - TCP
Text-to-Speech Services - TCP and UDP
• 35.175.185.150:3001
• 35.175.185.150:8000
• 44.212.88.215:8000
• 54.149.243.27:3001
• 54.149.243.27:8000
• 54.70.235.134:3001
• 54.70.235.134:8000
StratusFAX 2.0 - TCP
• 5066 TCP - HTTPS and HTTP
StratusMEETING - TCP and UDP
REMINDER: If your company does not use StratusMEETING, the subnets for this service do not need to be allowed.
• 54.188.133.147:3443
• 3.130.158.184:3443
• 35.183.150.146:3443
StratusHUB
REMINDER: If your company does not use the StratusHUB desktop app, the port for this service does not need to be opened.
• 8082 - TCP
StratusWEB PHONE
REMINDER: If your company does not use StratusWEB PHONE, the port for this service does not need to be opened.
• 9002 - TCP - websockets
Ports - Enswitch 1 and 2 Platforms
IMPORTANT: These ports only need to be opened if you are utilizing one of our Enswitch (ES1 or ES2) platforms. If you are using our Stratus platform, these ports do not need to be opened.
If you are not sure which service you are utilizing, contact your Installer or our Technical Support team for more information.
• 5060-5062 UDP - SIP
• 10,000-20,000 UDP - RTP
• 80, 443 TCP - HTTP/HTTPS
Push Notifications Ports
IMPORTANT: If your users are using our softphone mobile apps on cellular devices or tablets connected to the office's Wi-Fi network, it is recommended to open these ports on the firewall equipment so that push notifications for the apps are not blocked.
Android and Google Devices - Google's Firebase Cloud Messaging, aka FCM
• 443, 5228, 5229, 5230 - TCP
More Info: Ports 5228, 5229, and 5230 are the primary ports used by Google's Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM) service for mobile devices to receive push notifications.
Apple Devices - Apple Push Notification Service, aka APNs
• 5223, 443, 2197 - TCP
More Info: Port 5223 is the primary port for communication used by Apple's Push Notification Service (APNs).
Ports 443 and 2197 are used for sending notifications from Mobile Device Management (MDM) software to APNs and as a fallback on Wi-Fi if port 5223 cannot be utilized.
For more information on port forwarding and NAT rules on the MX, check out the following documentation curated by Cisco:
How Do I Configure the MX to Meet Requirements?
While using SpectrumVoIP as your VoIP phone system provider, we recommend adjusting the following settings on your network equipment to help optimize the performance of your desk phones.
Settings to Disable
-
SIP ALG (Application Layer Gateway) functions (NOT NEEDED FOR CISCO MERAKIS) such as SIP Transformations, SIP Application Helpers, SIP Normalization, etc..
Note: Cisco Meraki firewalls do not use an ALG function. Although your Cisco Meraki firewall does not use ALG, it is still important to make sure that any other network equipment that may be managing traffic does not have SIP ALG enabled either.
-
SPI (Stateful Packet Inspection) or DPI (Deep Packet Inspection) for the IP addresses of phones and voice VLANs.
NOTE: You can leave SPI and DPI enabled for all other devices. You would only need to disable SPI or DPI for the IP addresses of phones or a voice VLAN you have assigned your phones to.
- AV Client Enforcement on any IP address assigned to a phone
- Content Filtering on any IP address assigned to a phone
Settings to Enable
- Bandwidth Management/Traffic Shaping (See below for a list of our network blocks and bandwidth requirements)
- Default UDP session timeout set to 300 seconds
- Consistent NAT
-
Load balancing policy configured for ingress and egress of phones only utilizing the same WAN interface. (If applicable)
DANGER: We do NOT support the use of load-balancing for traffic entering and exiting multiple WAN interfaces.
For SD-WAN or Multi-WAN setups, please ensure that all traffic is being sent out through a single WAN interface, otherwise provisioning and directories may not work as intended.
-
Inbound and outbound traffic on ports and subnets listed below:
Recommended Subnet and Port Configuration
SpectrumVoIP Public Subnets
• 199.71.209.0/24
• 24.227.249.0/25
• 72.249.136.32/28
• 206.123.122.32/27
• 212.69.157.32/27
• 40.143.31.64/27
• 45.41.5.0/24
• 12.150.91.0/24Ports - Stratus Platform
IMPORTANT: These ports only need to be opened if you are utilizing our Stratus platform. If you are using our Enswitch (ES) platforms, these ports do not need to be opened.
If your company does not use the StratusHUB desktop app, the SpectrumVoIP Stratus mobile app, StratusMEETING, or StratusWEB PHONE, the ports/subnets for those services do not need to be allowed or opened.
If you are not sure which services you are utilizing, contact your Installer or our Technical Support team for more information.
Main Utilized Ports
• 5060-5062 UDP - SIP
• 20,000-40,000 UDP - RTP
• 80, 443 TCP - HTTP/HTTPSPortal Dynamic Updates
• 8001 - TCP
Text-to-Speech Services - TCP and UDP
• 35.175.185.150:3001
• 35.175.185.150:8000
• 44.212.88.215:8000
• 54.149.243.27:3001
• 54.149.243.27:8000
• 54.70.235.134:3001
• 54.70.235.134:8000StratusFAX 2.0 - TCP
• 5066 TCP - HTTPS and HTTP
StratusHUB Desktop App
REMINDER: If your company does not use the StratusHUB desktop app, the port for this service does not need to be opened.
• 8082 - TCP
StratusMEETING - TCP and UDP
REMINDER: If your company does not use StratusMEETING, the subnets for this service do not need to be allowed.
• 54.188.133.147:3443
• 3.130.158.184:3443
• 35.183.150.146:3443StratusWEB PHONE
REMINDER: If your company does not use StratusWEB PHONE, the port for this service does not need to be opened.
• 9002 - TCP - websockets
Ports - Enswitch 1 and 2 Platforms
IMPORTANT: These ports only need to be opened if you are utilizing one of our Enswitch (ES1 or ES2) platforms. If you are using our Stratus platform, these ports do not need to be opened.
If you are not sure which service you are utilizing, contact your Installer or our Technical Support team for more information.
• 5060-5062 UDP - SIP
• 10,000-20,000 UDP - RTP
• 80, 443 TCP - HTTP/HTTPSPush Notifications Ports
IMPORTANT: If your users are using our softphone mobile apps on cellular devices or tablets connected to the office's Wi-Fi network, it is recommended to open these ports on the firewall equipment so that push notifications for the apps are not blocked.
Android and Google Devices - Google's Firebase Cloud Messaging, aka FCM
• 443, 5228, 5229, 5230 - TCP
More Info: Ports 5228, 5229, and 5230 are the primary ports used by Google's Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM) service for mobile devices to receive push notifications.
Apple Devices - Apple Push Notification Service, aka APNs
• 5223, 443, 2197 - TCP
More Info: Port 5223 is the primary port for communication used by Apple's Push Notification Service (APNs).
Ports 443 and 2197 are used for sending notifications from Mobile Device Management (MDM) software to APNs and as a fallback on Wi-Fi if port 5223 cannot be utilized.
- DNS resolution for the phones
Are Application-Level Gateways Used by Cisco Meraki Firewalls?
No. Cisco Meraki firewalls do not utilize ALG, so SIP ALG does not need to be disabled for a Cisco Meraki.
Note: Although your Cisco Meraki firewall does not use ALG, it is still important to make sure that any other network equipment that may be managing traffic does not have SIP ALG enabled either.
ALG is a technology that allows a NAT used by a stateful firewall to dynamically assign ports and direct communication between endpoints. The MX security appliance of a Cisco Meraki is a full-featured stateful firewall that does not have any ALG functionality.
Can the UDP Timeout Value be Adjusted?
No. The MX has a UDP timer function that cannot be adjusted; however, this may not pose any issues since the default timeout for the UDP timer is 300 seconds. This allows a VoIP call to be idle for 5 minutes before the call may be dropped.
The UDP timer will drop a call after an extended period of inactivity. A timeout would require both peers to be entirely silent for an extended period of time in order to take effect, so it is unlikely that a call may be dropped due to timing out.
The MX and NAT Rules
To ensure VoIP calls are able to traverse your network to their intended destinations, it is recommended to set up NAT rules in the MX to allow traffic to pass through the subnets and ports used by SpectrumVoIP services.
To review the ports and IPs used by SpectrumVoIP services, review the module below:
Recommended Subnet and Port Configuration
SpectrumVoIP Public Subnets
• 199.71.209.0/24
• 24.227.249.0/25
• 72.249.136.32/28
• 206.123.122.32/27
• 212.69.157.32/27
• 40.143.31.64/27
• 45.41.5.0/24
• 12.150.91.0/24
Ports - Stratus Platform
IMPORTANT: These ports only need to be opened if you are utilizing our Stratus platform. If you are using our Enswitch (ES) platforms, these ports do not need to be opened.
If your company does not use the StratusHUB desktop app, the SpectrumVoIP Stratus mobile app, StratusMEETING, or StratusWEB PHONE, the ports/subnets for those services do not need to be allowed or opened.
If you are not sure which services you are utilizing, contact your Installer or our Technical Support team for more information.
Main Utilized Ports
• 5060-5062 UDP - SIP
• 20,000-40,000 UDP - RTP
• 80, 443 TCP - HTTP/HTTPS
Portal Dynamic Updates
• 8001 - TCP
Text-to-Speech Services - TCP and UDP
• 35.175.185.150:3001
• 35.175.185.150:8000
• 44.212.88.215:8000
• 54.149.243.27:3001
• 54.149.243.27:8000
• 54.70.235.134:3001
• 54.70.235.134:8000
StratusFAX 2.0 - TCP
• 5066 TCP - HTTPS and HTTP
StrtausHUB Desktop App
REMINDER: If your company does not use the StratusHUB desktop app, the port for this service does not need to be opened.
• 8082 - TCP
StratusMEETING - TCP and UDP
REMINDER: If your company does not use StratusMEETING, the subnets for this service do not need to be allowed.
• 54.188.133.147:3443
• 3.130.158.184:3443
• 35.183.150.146:3443
StratusWEB PHONE
REMINDER: If your company does not use StratusWEB PHONE, the port for this service does not need to be opened.
• 9002 - TCP - websockets
Ports - Enswitch 1 and 2 Platforms
IMPORTANT: These ports only need to be opened if you are utilizing one of our Enswitch (ES1 or ES2) platforms. If you are using our Stratus platform, these ports do not need to be opened.
If you are not sure which service you are utilizing, contact your Installer or our Technical Support team for more information.
• 5060-5062 UDP - SIP
• 10,000-20,000 UDP - RTP
• 80, 443 TCP - HTTP/HTTPS
Push Notifications Ports
IMPORTANT: If your users are using our softphone mobile apps on cellular devices or tablets connected to the office's Wi-Fi network, it is recommended to open these ports on the firewall equipment so that push notifications for the apps are not blocked.
Android and Google Devices - Google's Firebase Cloud Messaging, aka FCM
• 443, 5228, 5229, 5230 - TCP
More Info: Ports 5228, 5229, and 5230 are the primary ports used by Google's Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM) service for mobile devices to receive push notifications.
Apple Devices - Apple Push Notification Service, aka APNs
• 5223, 443, 2197 - TCP
More Info: Port 5223 is the primary port for communication used by Apple's Push Notification Service (APNs).
Ports 443 and 2197 are used for sending notifications from Mobile Device Management (MDM) software to APNs and as a fallback on Wi-Fi if port 5223 cannot be utilized.
For more information on port forwarding and NAT rules on the MX, check out the following documentation curated by Cisco:
Troubleshooting
The following section outlines some common VoIP issues that may arise, and some recommended troubleshooting steps to narrow down the issue.
One-Way Audio
Consider that voice communication typically happens as two simultaneous UDP streams, one for each direction of communication. These are two separate streams, as opposed to a single two-way stream. If communication in one direction is not reaching the peer, then the symptom is usually that only one party can hear the other's audio.
To address this issue, check the following:
- Trace the flow of traffic, and check any firewalls to ensure they are not blocking traffic.
- If a stateful firewall like the MX is passing traffic between the two peers, ensure there are appropriate mechanisms in place to allow inbound communication (1:1 NAT, port forwarding, etc).
- If it's unclear exactly where the traffic is being dropped, determine based on the symptoms which direction of traffic seems to be failing, and take packet captures at network hops to see where the flow stops.
- If the PBX is configured to require an ALG (discussed above), and that traffic is going through an MX, it may be dropped in one direction. In this case, refer to the PBX-specific documentation for means to address NAT without ALG.
Poor Audio Quality
Due to the sensitive nature of VoIP traffic, low voice quality (or "jitter") may be experienced due to interruptions in traffic flow or bandwidth limitations.
To improve voice quality, ensure that the following best practices are in place:
- Make sure voice traffic is segregated to its own voice VLAN, so normal data cannot interfere.
- Check the network's bandwidth limitations and ensure there's enough bandwidth (as recommended/required by the voice system).
- Use traffic shaping/QoS where necessary, in the event that a link on the network is being saturated.
- Take packet captures to get an idea of call quality, and where it is degraded. Many capture analysis tools, including Wireshark, have the ability to perform RTP analysis.
Take note of the "symptoms" exhibited in a poor-quality phone call. Specific traits of the call can help narrow down the issue. Please refer to this guide for a breakdown of different call quality symptoms.
Phones Cannot Obtain an IP Address/Configuration
Typically, VoIP equipment will get a dynamic configuration from a TFTP server or other service on the network. This will commonly be levied by a DHCP server, where leases to VoIP endpoints will include voice-specific DHCP options. In the event that the phone fails to connect to the network/get a working configuration, consider the following recommended steps:
- If a separate voice VLAN is being used, ensure that phones are being put on the appropriate VLAN by means of an access port, voice VLAN configuration on the port, or even configured on the phone itself.
- If this is being done, ensure that a DHCP server is up and running on that VLAN, and configured with the appropriate scope and options.
- If phones have a working IP configuration on the network (or a static assignment is given for test purposes) and are told to get their VoIP configuration from some other server, ensure that the server is online and reachable from the voice VLAN.